08 Jan 2025 Strengthen Your Data Governance with Data Catalog
This blog post is part of our data governance blog mini-series. In our first post, we introduced the concept of Data Governance (DG) as a driver to achieving data excellence, and outlined the importance of focusing on tangible, outcome-driven initiatives when implementing DG. It’s much more than a theoretical exercise involving data, roles, and ownership; it covers essential technical domains like Data Catalog, Data Quality, Master Data Management (MDM), and DevOps. In this article, we’ll explore the Data Catalog domain in depth, examining how it strengthens DG by ensuring trust, quality, transparency and accessibility throughout your organisation.
A Data Catalog acts as a centralised repository, providing a detailed inventory of data assets enriched with metadata. Integrating DG with a Data Catalog creates a synergistic relationship that enhances data management practices, allowing organisations to align policies with metadata, improve data quality, enhance security, facilitate compliance, and enable effective data stewardship. By bridging the gap between technical and business users, a Data Catalog plays a crucial role in making DG more effective and impactful, as we will see in this article. To learn more about Data Governance as a whole, take a look at the first part of this mini-series here.
GlobalLogic example
GlobalLogix’s Data Catalog includes detailed metadata for assets, ranging from container tracking data in maritime logistics to inventory levels in warehousing. It also identifies who owns each dataset—whether it’s the IT department for system logs or the Quality department for performance metrics—ensuring accountability and clear lines of responsibility.
Streamlining Operations with a Data Catalog
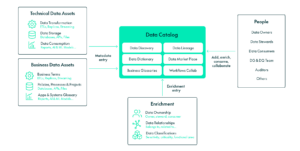
A Data Catalog is a detailed centralised repository of data assets owned by a company. It includes metadata, data sources, structures, usage and relationships, and helps users to understand their data as they can explore, comprehend, and utilise it more effectively.
Scope of a Data Catalog
A Data Catalog compiles and organises enriched metadata from a wide set of technical data assets alongside business information, as well as details on data ownership, classification, and relationships. It empowers all kinds of users to harness multiple features built upon the enriched data provided.
GlobalLogic example
To make the concepts in this article clearer, we will follow a practical example involving a fictional logistics company. This example will help illustrate how a Data Catalog can address common challenges in data governance.
Let’s imagine a large logistics company called GlobalLogix that operates across multiple business areas, including global logistics, maritime, air, rail, and terrestrial logistics, as well as port terminals and warehousing. Additionally, the company has several corporate departments like Finance, IT, Marketing, and Quality. The company faces significant challenges in unifying business concepts across these diverse areas, ensuring data quality, and enabling effective collaboration between its operational and corporate teams. In this article, we’ll explore how GlobalLogix can implement a Data Catalog as a key part of its Data Governance strategy to address these issues, ultimately improving trust in its data and empowering its business teams.
Key Features of a Data Catalog
A Data Catalog provides various features to enhance data management and utilisation:
- Data Dictionary: This feature offers detailed descriptions of data assets, including metadata about systems, tables, reports, and classifications. It helps users to understand the context and structure of data, preventing misunderstandings and ensuring accurate use.
- Data Discovery: The search functionality allows users to quickly find relevant data by using keywords, tags or filters, streamlining access to critical information and improving overall efficiency.
- Business Glossaries: These glossaries standardise business terminology and practices, ensuring that key terms, processes, and KPIs are consistently understood and applied across all departments.
Advanced features include:
- Data Lineage: This feature provides a visual representation of the data journey through various systems, helping users understand its transformations, enabling better auditing, and supporting more informed decision-making.
- Data Marketplace: The data marketplace acts as a centralised platform for sharing and accessing curated, trusted datasets, ensuring that teams work with reliable, approved data for analytical and reporting needs.
GlobalLogic example
At GlobalLogix, the Data Catalog has proven invaluable across departments. The data dictionary ensures clarity between fields like “weight_kg” and “gross_weight_kg”, preventing confusion during report building. Data Discovery allows users from Warehousing to quickly find data on inventory turnover, while the Business Glossary helps align definitions of key terms between Marketing and Finance. Advanced features like Data Lineage help the Quality department to trace data discrepancies, and the Data Marketplace enables Finance to access preapproved datasets for accurate financial forecasting.
Benefits of a Data Catalog
Implementing a Data Catalog addresses several common challenges organisations can face:
- Data Discovery: A Data Catalog enhances data visibility, allowing users to quickly locate datasets, reports and systems, improving efficiency and decision-making.
- Data Context: It provides the necessary context by linking data to its sources and transformations, helping users to understand the origins and logic behind the data, speeding up issue resolution and impact analysis.
- Business Definitions and KPI Alignment: This standardises critical business definitions and KPIs across departments, ensuring consistency in metrics, compliance with regulations, and clarity in data security and access management.
- Collaboration Efficiency: By streamlining communication channels and defining clear ownership of data assets, implementing a Data Catalog facilitates collaboration between departments and improves the overall quality of shared data.
Building Data Trust with a Data Catalog
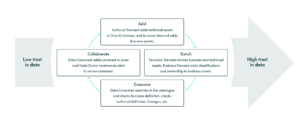
Achieving high data trust within a Data Catalog involves a series of well-defined steps to ensure data is reliable, accessible, and understandable. This process can be broken down into four key stages: Add, Enrich, Consume, and Collaborate. Each stage plays a crucial part in transforming low-trust data into high-trust data, as illustrated in this operational process diagram:
GlobalLogic example
Add: Warehousing adds the “Inventory Turnover Rate” term to the catalogue, linking it to relevant stock and sales data for consistency across departments.
Enrich: The Quality team classifies the data into “High Turnover Products” and “Low Turnover Products”, while IT links these business terms to technical data tables for accurate reporting.
Consume: The Finance department uses the catalogue to verify turnover rates for financial forecasts, ensuring data accuracy and relevance.
Collaborate: After discovering discrepancies, the Warehousing team flags the issue, and IT corrects the syncing process, updating the catalogue and preventing future errors.
By systematically adding, enriching, consuming, and collaborating on data, organisations can transform their Data Catalog into a high-trust resource, driving better business outcomes and effective decision-making.
Data Catalog Technologies
There are various tools available to implement a Data Catalog, each offering different functionalities. These technologies typically automate the management of data dictionaries, business glossaries, data discovery and data lineage, effectively streamlining data governance practices.
- Data Dictionary – Auto Entry: Tools scan data sources and automatically populate the data dictionary with metadata, reducing the need for manual entry.
- Business Glossary: A centralised glossary helps standardise business terms, promoting clarity across departments.
- Data Discovery: Advanced search capabilities allow users to quickly find relevant data assets across multiple systems, significantly speeding up the discovery process.
- Data Lineage: Visual representations of data flows provide insights into how data moves and transforms, assisting with compliance and auditing.
- Data Marketplace: Users can request and access curated, high-quality datasets.
- Workflow Collaboration: Dedicated tools support custom workflows for collaboration on data management projects, ensuring all stakeholders are aligned.
- Data Quality and MDM: Features ensure data accuracy and consistency through built-in data profiling and MDM capabilities.
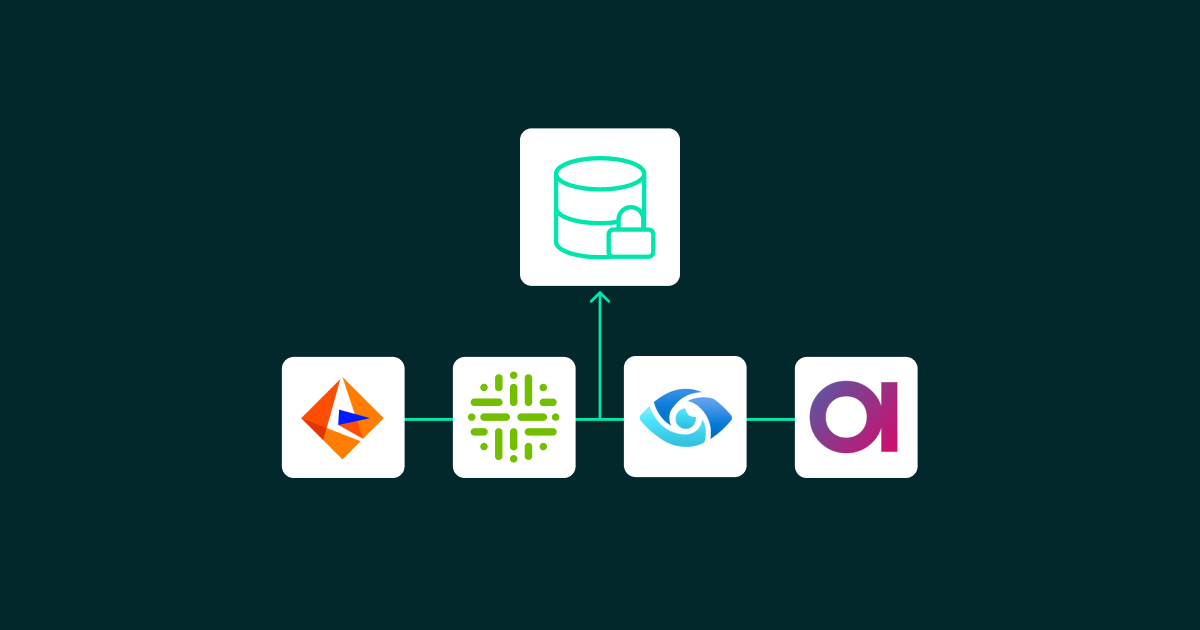
Example Tools
- Informatica: A powerful platform known for its data management capabilities, including data quality checks, MDM and lineage tracking, ideal for complex environments.
- Collibra: A highly scalable solution focused on data governance, offering strong collaboration and workflow features for detailed governance across business units.
- Ataccama: A unified platform that combines data governance, quality management and MDM, for organisations that need to maintain strict data standards across various environments.
- Purview: A comprehensive data governance solution providing faultless integration with Azure and Microsoft 365, whilst enabling data stewardship, data discovery, lineage tracking, and compliance.
Conclusions
The importance of an effective data governance policy cannot be overstated, and a well-implemented Data Catalog is a cornerstone of this strategy, acting as a centralised repository that enhances the visibility, accessibility, and trustworthiness of an organisation’s data assets. Gaining trust and visibility is crucial for ensuring that all stakeholders across the organisation can rely on its data for critical decision-making.
In this article, we’ve explored the Data Catalog’s fundamental role in addressing common data management challenges, such as data discovery, context, alignment on business definitions, and inefficient collaboration. By systematically adding, enriching, consuming, and working together on data, organisations can transform their Data Catalog into a high-trust resource that drives better business outcomes and optimised decision-making.
We’ve also looked at various technologies available for implementing a Data Catalog, each offering unique features and capabilities. The choice of the right technology will depend on the specific needs of your organisation, as well as its existing infrastructure, the level of collaboration required, and any regulatory requirements.
GlobalLogic example
The implementation of a Data Catalog at GlobalLogix has significantly improved the company’s ability to manage and govern data across its various business areas. By unifying business concepts, establishing clear responsibilities for data quality and enhancing collaboration, the catalogue has become an essential tool for ensuring that all departments are aligned and working with reliable, consistent information. This centralised approach to data governance not only reduces operational risks but also empowers teams to make informed decisions that drive the company’s strategic objectives.
In conclusion, as data continues to grow in volume and complexity, the role of the Data Catalog will only become more critical. Organisations that invest in robust Data Catalog solutions today will be better equipped to harness the full potential of their data, ensuring that they remain agile, compliant, and innovative in a competitive landscape.
Here at ClearPeaks, we understand that no two businesses are alike, and a one-size-fits-all approach simply doesn’t work when it comes to data solutions. With a proven track record, we’re committed to empowering your organisation with the tools and insights needed to foster collaboration, build trust, and drive innovation. Don’t let the complexities of data governance hold you back—contact us today to see how we can help you turn your data into a strategic advantage!